Seeking Interventional Radiology Care?
Interventional Radiology Care Serving Oxon Hill, Waldorf, Springfield & The Whole DMV
With a focus on comprehensive patient care, VidaVascular offers minimally-invasive vascular care for fibroids, knee pain, hemorrhoids, varicose veins, and arterial disease. We're on a mission to serve Oxon Hill, Waldorf & Springfield Areas with convenient access to care solutions for you and your family's health needs accessibly on the same or next day.
Convenient Interventional Radiology Care Practice Locations Serving The Whole Greater Oxon Hill, Waldorf, and Alexandria Regions
Our Comprehensive Medical Services

Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
Minimally invasive UFE shrinks fibroids to reduce heavy bleeding, pain, and pressure.
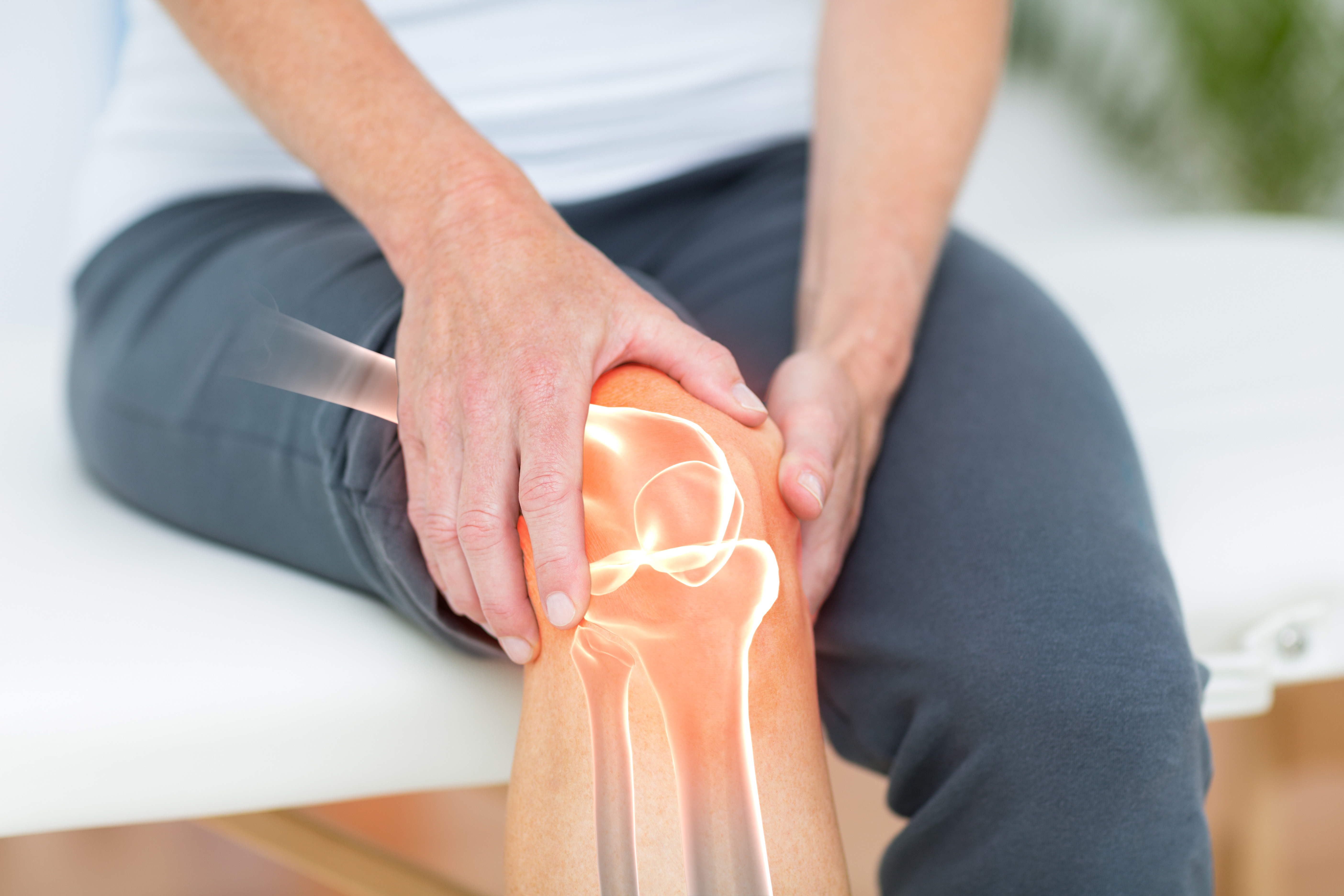
Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE)
GAE targets knee inflammation to help reduce osteoarthritis pain and improve function.
Hemorrhoid Artery Embolization (HAE)
HAE reduces blood flow to bleeding hemorrhoids to ease symptoms with minimal downtime.
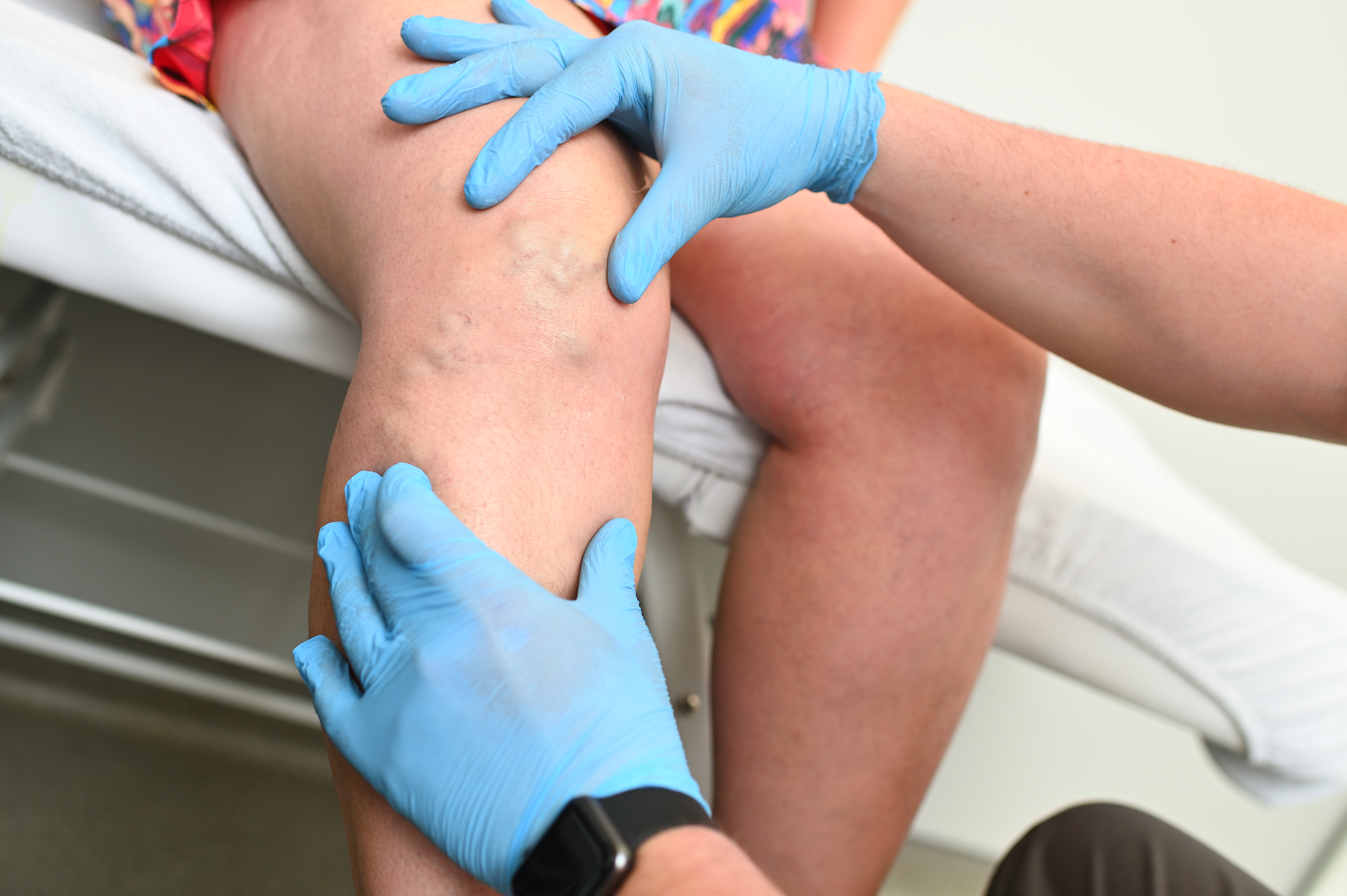
Varicose Veins & Endovenous Ablation
Endovenous ablation treats vein reflux to relieve varicose vein heaviness and swelling.
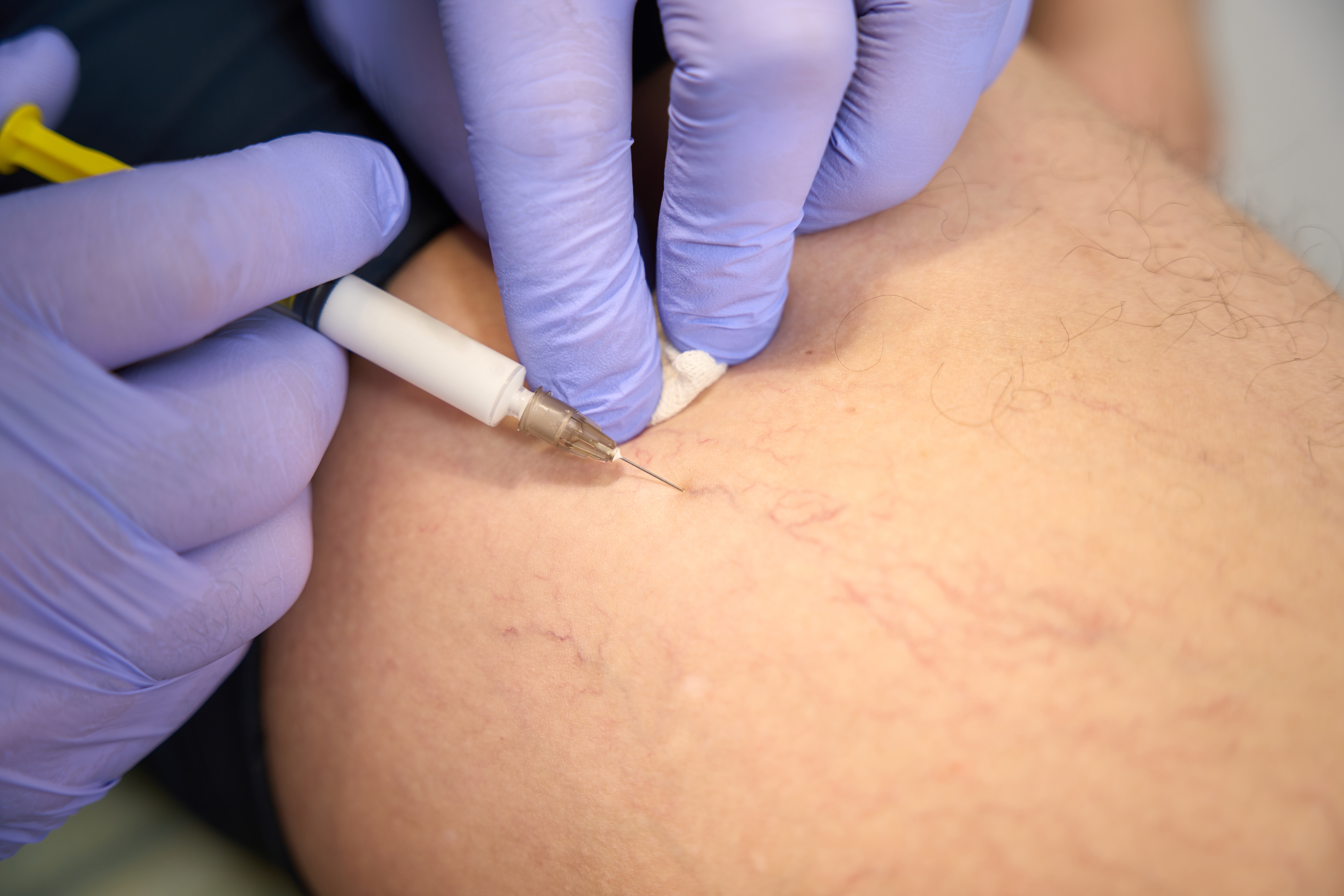
Spider Veins & Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy fades spider veins by closing tiny surface veins for smoother looking legs.
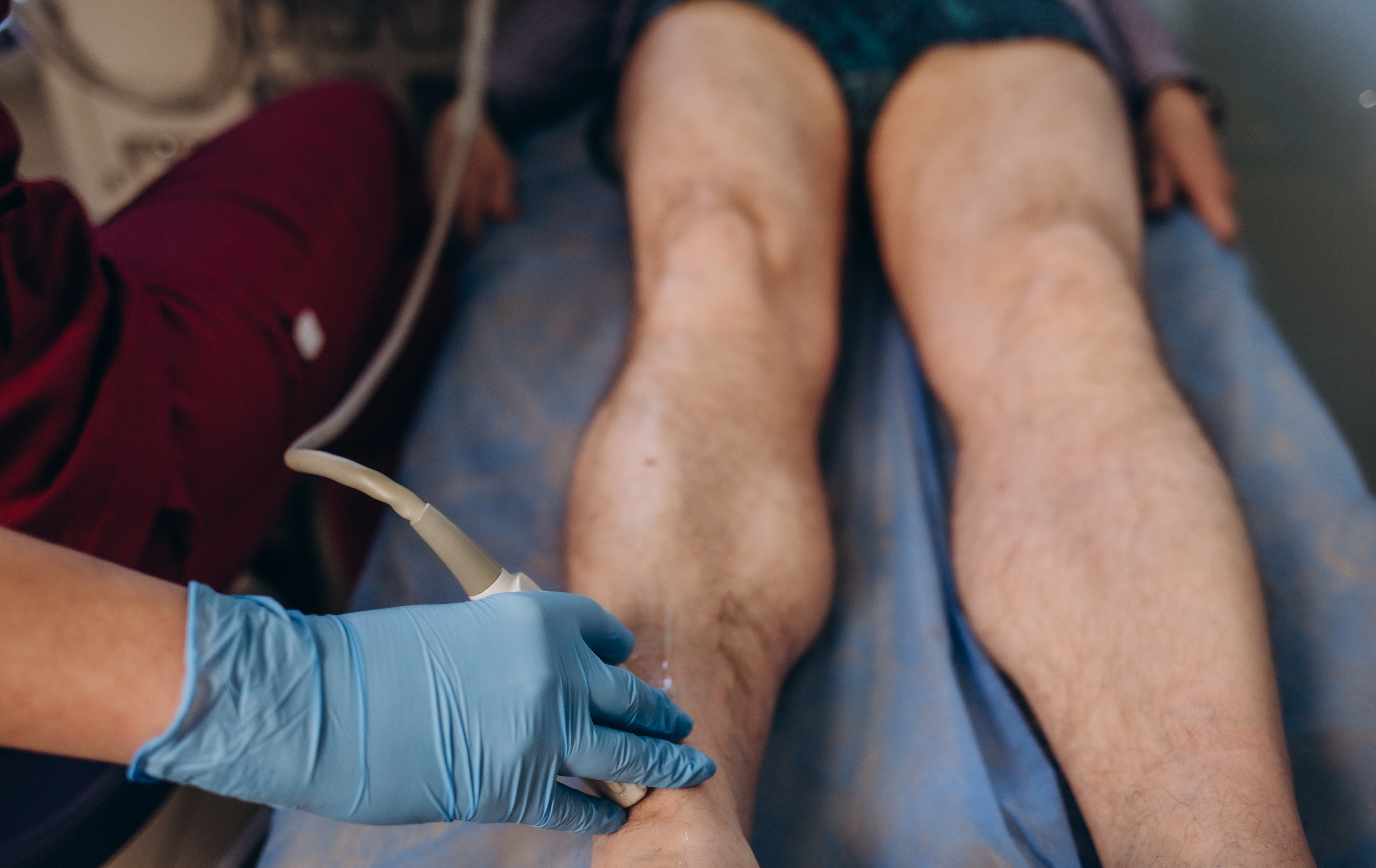
Walk-in Rule-out
DVT
Walk in rule out DVT evaluation with vein ultrasound when needed for fast, safe answers.

Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
PAD evaluation and treatment to improve leg circulation, walking comfort, and vascular health.
Ready to get the care your deserve?
Every single visit, you’ll be met with expert care, real compassion, and a plan that fits your life.

Welcome to VidaVascular
A Patient-Centered Approach To Care For Individuals & Families Throughout The Greater Oxon Hill Area.
VidaVascular is committed to serving patients in and around the Oxon Hill area with advanced, minimally invasive vascular and interventional care. Our team provides outpatient treatments using ultrasound guidance in a safe, patient-centered setting. Many procedures are performed under local anesthesia with intravenous sedation when appropriate, and are designed to help patients avoid larger incisions and lengthy recovery times. We take the time to answer questions, explain options clearly, and help patients feel comfortable every step of the way.
Experienced Providers
Our seasoned physicians and providers form a multi-disciplinary team to fully cover you and your family's care.
Quality & Time
We're built on a vision of patient-centric care, where providers spend more time with patients to deliver true quality care.
Convenience
With multiple sites, rapid availability, and accepting most insurances, we serve our community with the most accessible care.
What Our Patients Are Saying
Insurances We Accept
We accept most insurance providers. If you have specific questions regarding your coverage, please contact us for additional information.
Access The Convenient Care You Deserve
Get In Touch
Call, click, or visit — we’re here to make getting care simple & stress-free!
251 National Harbor Blvd, Suite 104 Oxon Hill, MD 20745
Get In Touch
Call, click, or visit — we’re here to make getting care simple & stress-free!
6120 Brandon Ave, Suite 216, Springfield, VA 22150
Get In Touch
Call, click, or visit — we’re here to make getting care simple & stress-free!
4255 Altamont Place, Suite 101, White Plains, MD 20695
Our Promise to You
To provide advanced, personalized care with skill, compassion, and respect—every time you visit. You’re not just a condition to treat; you’re a whole person with unique goals and challenges, and we’re here to help you overcome them.
We’re committed to serving our community with integrity and heart, combining innovation with genuine connection—because true healing goes beyond checklists.
© 2026 VidaVascular | Accessibility | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Policy | Powered by DoctoGrow





